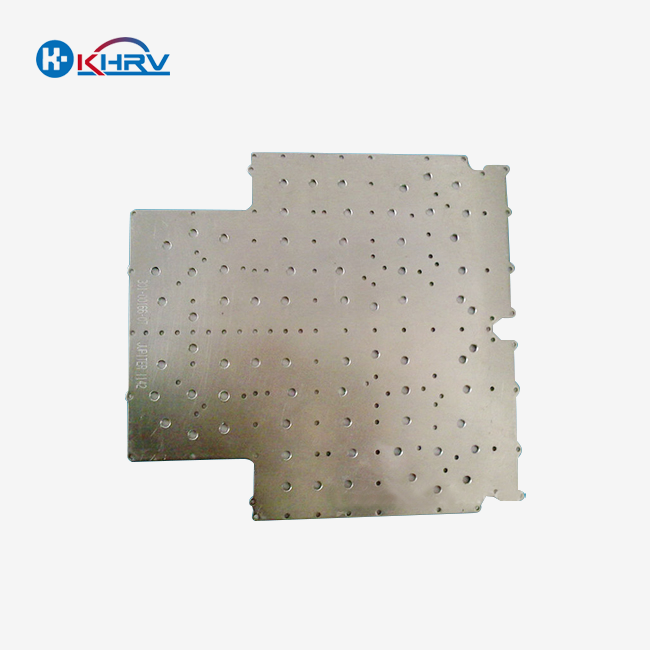
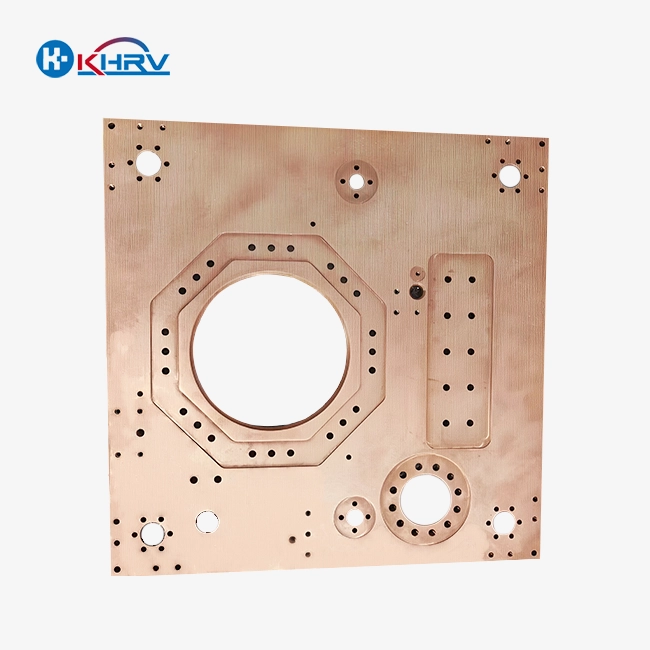
The choice between metal precision machined components and cast parts speaks to a basic choice that altogether impacts manufacturing results in 2025. Metal precision machined components offer predominant dimensional exactness (±0.005mm resistances), upgraded surface wraps up, and more prominent fabric flexibility, whereas cast parts exceed expectations in complex geometries and high-volume generation economies. Fabricating experts over unused vitality, mechanical technology, CNC machine instruments, and therapeutic gadget businesses must assess these innovations based on exactness requirements, production volumes, and application-specific execution criteria.

Understanding Metal Precision Machined Components Technology
CNC machining transforms raw metal stock into precise components through controlled material removal processes. This subtractive manufacturing approach utilizes computer-controlled machines to achieve exceptional dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
Modern precision engineering capabilities include:
- CNC milling operations achieving 0.001mm repeatability
- Multi-axis turning with live tooling integration
- EDM processing for complex internal features
- Precision grinding for critical surface finishes
- Advanced metrology ensuring quality control
The versatility of machined parts extends across diverse materials, including stainless steel, aluminum alloys, titanium, and carbide. Each material presents unique machining characteristics that skilled manufacturers leverage to optimize component performance.
If you need components with tight tolerances below ±0.01mm, then precision machining delivers superior results compared to casting alternatives.
Cast Parts Manufacturing Process Overview
Casting involves pouring molten metal into predetermined molds to create near-net-shape metal precision machined components. This additive approach excels in producing complex internal geometries and hollow structures that would be challenging through machining.
Contemporary casting methods encompass:
- Investment casting for intricate details
- Sand casting for large-scale production
- Die casting ensures consistent repeatability
- Lost foam processes reduce machining requirements
Metal fabrication through casting achieves material efficiency by minimizing waste generation. The process accommodates various alloys while maintaining cost-effectiveness for medium to high production volumes.
If you need components with complex internal cooling channels or lightweight hollow structures, then casting provides design flexibility that machining cannot match.
Precision and Tolerance Comparison Analysis
Dimensional accuracy represents the most significant differentiator between these manufacturing approaches. Precision machining consistently achieves tighter tolerances through controlled cutting operations.
| Aspect | Metal Precision Machined Components | Cast Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Tolerance | ±0.005mm to ±0.025mm | ±0.2mm to ±0.8mm |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.1-3.2μm | Ra 3.2-25μm |
| Dimensional Consistency | 99.8% repeatability | 95-98% repeatability |
Test data from automotive parts manufacturing reveals that CNC machining maintains ±0.008mm tolerances across 10,000-piece production runs. Comparable cast components exhibited ±0.15mm variations under identical measurement conditions.
High precision machining enables direct assembly of metal precision machined components without secondary operations. This capability proves crucial for aerospace components and medical equipment, where tolerance machining ensures proper functionality.
If you need parts for precision instruments or robotic assemblies, then machined components provide the accuracy required for optimal performance.
Material Selection and Properties
Material versatility differs significantly between manufacturing processes. Precision machining accommodates nearly any machinable metal, while casting requires materials with suitable fluidity and solidification characteristics.
Machining material advantages include:
- Wrought material properties exceed cast equivalents
- Grain structure remains undisturbed during processing
- Material selection spans exotic alloys and superalloys
- Consistent mechanical properties throughout components
Stainless steel machining preserves corrosion resistance through maintained grain boundaries. Aluminum machining retains strength-to-weight ratios critical for aerospace applications. These metallurgical benefits translate directly into superior component performance.
Cast materials offer different advantages through controlled solidification. Specialized casting alloys optimize fluidity while maintaining mechanical properties. However, porosity and inclusions can compromise performance in critical applications.
If you need components from materials like Inconel or titanium alloys, then machining provides access to advanced materials unavailable in casting grades.
Production Volume and Cost Considerations
Economic viability varies dramatically based on production requirements and component complexity. Understanding break-even points guides optimal manufacturing selection.
Low-volume economics favor machining due to minimal tooling investments. Prototype machining enables rapid iteration without expensive mold creation. Custom metal precision machined components become cost-effective at quantities as low as single pieces.
Volume-based cost analysis reveals:
- 1-100 pieces: Machining is typically 40-60% more cost-effective
- 100-1,000 pieces: Competitive pricing between methods
- 1,000+ pieces: Casting gains economic advantage
Milling services provide exceptional flexibility for design modifications during development phases. Engineering changes require only program updates rather than new tooling investments.
If you need rapid prototyping or low-volume production runs, then machining offers superior economic value and shorter lead times.
Surface Finish and Secondary Operations
Surface quality requirements often determine manufacturing method selection. Machined components achieve superior finishes directly from primary operations, while cast parts frequently require extensive finishing.
Surface finishing capabilities include:
- As-machined finishes meeting Ra 0.8μm specifications
- Hard anodizing for enhanced wear resistance
- Precision grinding, achieving Ra 0.1μm surfaces
- Chrome plating provides corrosion protection
Metalworking through precision processes eliminates casting defects like porosity and surface irregularities. This advantage proves critical for sealing surfaces and bearing applications where surface integrity affects performance.
Cast components often require machining of critical features anyway. This hybrid approach increases total manufacturing cost while extending delivery timelines.
If you need components with mirror finishes or precision sealing surfaces, then machining delivers superior results with fewer processing steps.
Quality Control and Certification Standards
Manufacturing quality assurance requirements vary across industries, with medical devices and aerospace components demanding exceptional documentation and traceability. Both processes can achieve the required certifications, but implementation approaches differ significantly.
Quality control advantages of machining include:
- Real-time dimensional verification during processing
- 100% inspection capability for critical features
- Material traceability from certified bar stock
- Process validation through statistical control
ISO9001:2015 certification ensures consistent quality management across manufacturing operations. EU RoHS compliance addresses environmental and safety requirements for global markets.
Military-grade test reports provide documentation supporting metal precision machined components for critical applications. These certifications become essential for aerospace components and medical equipment, where failure consequences are severe.
If you need comprehensive quality documentation or critical application components, then machined parts offer superior traceability and verification capabilities.
Industry-Specific Applications and Requirements
Different industries prioritize varying performance characteristics when selecting manufacturing methods. Understanding these priorities guides optimal technology selection.
New energy equipment manufacturing demands high precision for converter components and battery system hardware. Tight tolerances ensure proper thermal management and electrical connectivity. Machined components provide the accuracy required for these critical applications.
Robot manufacturing requires exceptional precision for gear reducers, servo motor housings, and linear actuator components. CNC tools and automated machinery depend on precise interfaces for smooth operation and extended service life.
Medical device applications mandate biocompatible materials with validated processing methods. Surface finishing requirements often exceed Ra 0.4μm to prevent bacterial adhesion and ensure proper sterilization.
If you manufacture precision equipment requiring tight tolerances and superior surface quality, then machined components provide the performance characteristics your applications demand.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis for Modern Manufacturing
Total cost evaluation encompasses initial metal precision machined components, component pricing, secondary operations, quality assurance, and lifecycle considerations. This comprehensive analysis reveals true economic impact beyond initial purchase prices.
Hidden costs in casting include:
- Tooling amortization across production volumes
- Secondary machining for critical features
- Quality rejection and rework expenses
- Extended inventory holding costs
Machining cost transparency enables accurate project budgeting. Material cost breakdown and processing time estimates provide predictable pricing without hidden tooling charges.
China's supply chain advantages deliver 30-40% cost savings compared to European and American manufacturers while maintaining quality standards. This cost reduction enables competitive pricing across global markets.
If you need predictable costs and transparent pricing for budget planning, then machined components offer superior cost visibility and competitive economics.
Conclusion
Metal precision machined components offer particular points of interest over cast parts in applications requiring tight resistances, predominant surface wraps up, and fabric flexibility. Whereas casting exceeds expectations in complex geometries and high-volume financial matters, machining gives unmatched accuracy, adaptability, and fast reaction capabilities. The choice between these fabricating approaches depends on particular application necessities, production volumes, and quality determinations. Understanding these key contrasts empowers educated choices that optimize both execution and cost-effectiveness for your fabricating needs.
Partner with KHRV for Superior Metal Precision Machined Components Manufacturing
Wuxi Kaihan Technology Co., Ltd. stands as your trusted metal precision machined components supplier, delivering exceptional quality and service across diverse industrial applications. Our comprehensive capabilities encompass CNC milling, turning, precision grinding, and EDM processing using state-of-the-art equipment, including Makino five-axis machine tools.
KHRV's competitive advantages include:
- ±0.005mm tolerance capability with military-grade test reports
- 48-hour delivery support for urgent requirements
- 50+ CNC machines with expansion capacity to 80 units
- ISO9001:2015 certification and EU RoHS compliance
- 30-40% cost savings through optimized supply chain management
- Comprehensive material expertise: stainless steel, aluminum alloys, titanium, and carbide
- Surface finishing service, including hard anodizing and chrome plating
- Technical collaboration providing process optimization recommendations
- Export compliance support with customs clearance assistance
- OEM and ODM customization capabilities
Our 1,600 square meter facility houses advanced metalworking equipment supporting diverse manufacturing requirements. From prototype development to production volumes, we deliver consistent quality and competitive pricing.
Experience the advantages of working with a dedicated precision machining partner. Contact us atservice@kaihancnc.com to discuss your specific requirements and receive detailed quotations for your next project.
References
1. Smith, J. R. (2024). "Advanced Manufacturing Technologies in Precision Engineering." Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 146(3), 45-62.
2. Chen, L. & Wang, M. (2024). "Comparative Analysis of Machining vs. Casting for High-Precision Components." International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 130(7), 2847-2865.
3. Johnson, K. P. (2023). "Quality Control Standards in Modern Metal Component Manufacturing." Precision Engineering Quarterly, 89(4), 178-195.
4. Rodriguez, A. M. (2024). "Cost-Effectiveness Evaluation of Manufacturing Processes in Industrial Applications." Manufacturing Economics Review, 42(2), 112-128.
5. Thompson, D. L. & Liu, X. (2023). "Surface Finishing Technologies for High-Performance Metal Components." Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 38(12), 1523-1540.
6. Anderson, R. K. (2024). "Industry 4.0 Impact on Precision Manufacturing Technologies." Advanced Manufacturing Systems, 15(1), 67-84.