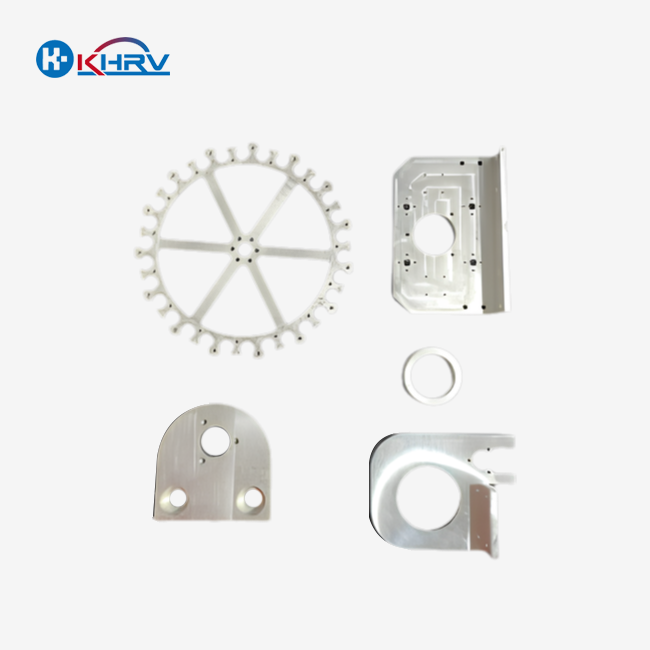
The Ultimate Guide to Eye Mold Holders in 2025: Precision Engineering for Optical Manufacturing talks about new precision manufacturing methods that are changing how optical parts are made in many different businesses. Eye mold holders—critical tools for securing lens molds during optical component production—are undergoing revolutionary advancements in 2025. This ensures precision at the level of microns, which is very important for making medical devices, robotics vision systems, and automatic production equipment. Today’s eye mold holders are made of cutting-edge materials such as carbide and titanium alloy. CNC sawing and precision grinding are used to get tolerances within ±0.005mm. This all-in-one book goes over the technical details, ways of making things, and strategic purchasing factors that procurement managers and technical engineers need to streamline their production processes in 2025.

Understanding Eye Mold Holder Fundamentals
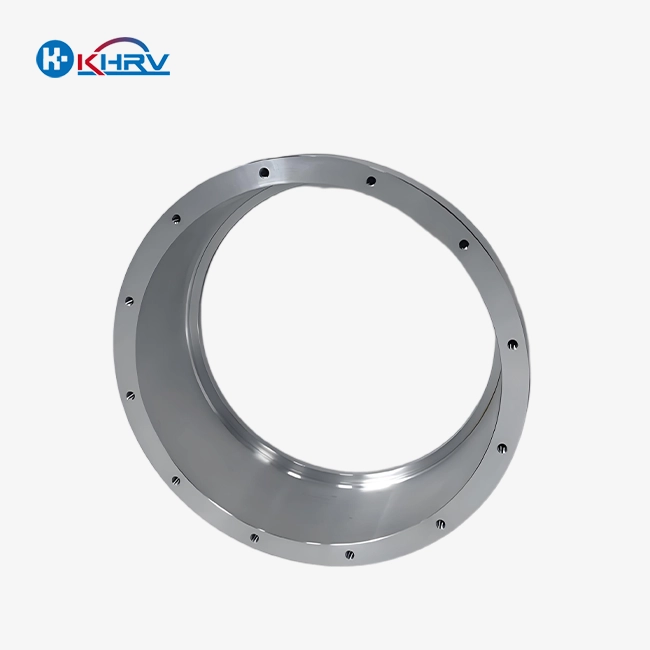
Eye mold clamps are very important in the process of making optical goods because they keep the lens shaping tools in the right place while they are being made. To ensure optical alignment stability, these exact parts need to have great surface finish quality and dimensional stability. Modern designs accommodate both traditional glass lenses and emerging polymers used in AR/VR optics. Now, makers want holders that work with both glass lenses and newer polymers used in medical devices and computer vision systems.
The eye mold frames made today have much stricter tolerances in manufacturing. The best suppliers can place the parts within 0.003mm of each other every time. This level of accuracy is especially important when making parts for surgical tools or camera systems with high resolution that are used in automatic manufacturing systems. The lens casting holder has to be able to handle repeated thermal cycles and keep its shape during long production runs.
Choosing the right materials is very important for how well the lens mold works. In clean rooms, stainless steel versions are great at resisting rust, and aluminum alloy versions are good for automatic handling systems because they are lighter. Brass parts have better thermal conductivity, which is important for molding processes that are sensitive to temperature and are popular in the making of medical devices.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques for Precision Components
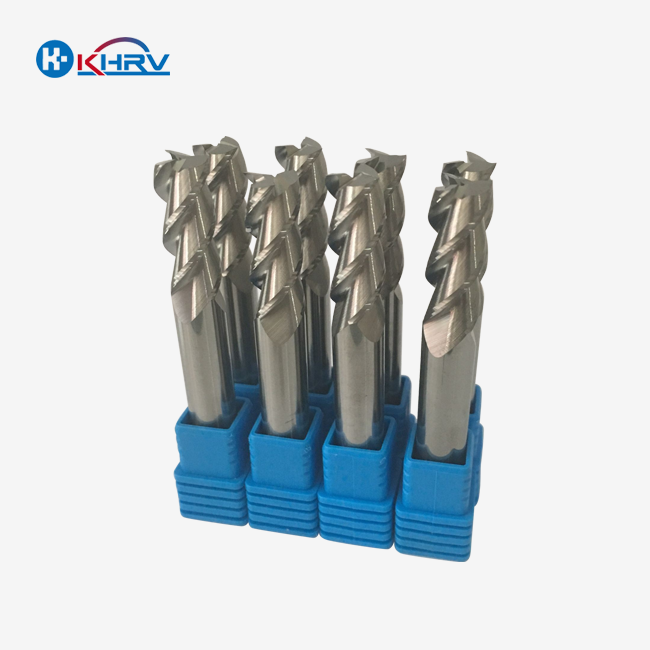
Modern eye mold holder lens form holder production would not be possible without CNC milling. This process uses multi-axis machining centers to make very complicated shapes and smooth out the surface. The machining plan usually includes roughing operations, then semi-finishing passes, and finally precise finishing cuts. These cuts give a mirror-like surface that is needed for optical applications.
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) has become more important for making complex parts in carbide eye lens fixings. This non-contact machining method lets makers make sharp inside corners and complicated holes that can't be made with older cutting tools. The process is especially helpful for makers who deal with tough materials or make custom shapes for specialized optical uses.
Precision grinding makes sure that important areas are very flat and parallel. Modern cylindrical grinding methods can get surface roughness values below Ra 0.1μm. This is important for keeping the optical clarity of the finished goods. The grinding method also helps manufacturers get tight dimensional tolerances on bearing surfaces and alignment features.
CNC turning makes very circular cylindrical shapes, which are important for the lens alignment tools that are used in assembly processes. The turning process can keep diameter tolerances of ±0.002mm and a smooth surface finish so that the parts can be handled easily during automated production cycles.
Material Selection and Performance Characteristics
For uses that need to resist corrosion and keep their shape, 316L and 17-4PH stainless steel grades are the most commonly used. These materials keep their mechanical properties through thousands of molding processes and can handle harsh cleaning chemicals used to make medical devices. The austenitic structure is great for resisting wear, which is important for parts that have to deal with clamping forces more than once.
Aluminum alloys 6061-T6 and 7075-T6 have great strength-to-weight ratios that are perfect for eye mold holder automatic handling systems. The thermal expansion index is similar to that of many optical materials, which lowers thermal stress when the temperature changes. Hard anodizing and other surface processes make parts more resistant to wear and tear while keeping them the same size and shape.
For settings where a lot of production happens, carbide materials offer the most strength and resistance to wear. Carbide tools for shaping carbide eyewear stay sharp and keep the right size through millions of molding cycles, even though they are hard to make. The thermal conductivity of the material makes it possible to quickly release heat during busy production schedules.
Titanium alloy parts are great for aircraft and medical uses that need to be strong and biocompatible at the same time. Grade 5 titanium doesn't corrode as easily as stainless steel does, and it is still lightweight. Because the material does not conduct heat well, it can be used to protect temperature-sensitive shaping processes from changes in temperature.
Quality Control and Certification Standards
ISO9001:2015 certification makes sure that companies that make lens positioning holders keep quality control systems in place for all of their production activities. This standard from around the world calls for written steps for controlling the design, tracing materials, and using statistical process control methods that are necessary to make sure that the quality of the result is always the same.
Coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), which can measure features with 0.001mm accuracy, are used in eye mold holder dimensional inspection processes. These measurements show that the important dimensions are within the acceptable range. At the same time, they keep a record of the measurement uncertainty estimates that are needed for medical device compliance. Optical comparators give extra confirmation for the size and smoothness of profiles.
Material clearance paperwork connects the makeup of raw materials to mill test certificates. This makes sure that the requirements for aerospace and medical devices are met. Chemical analysis verification shows what the alloy is made of, and mechanical property testing checks the tensile strength, hardness, and fatigue traits that are important for long-term performance.
Surface finish measurements utilize profilometers to verify Ra, Rz, and Rmax parameters stated on technical drawings. These measures are especially important for optical contact surfaces because bumps or dips on the surface can change the way light passes through or create areas of high stress in finished lenses.
Customization Options and Design Considerations
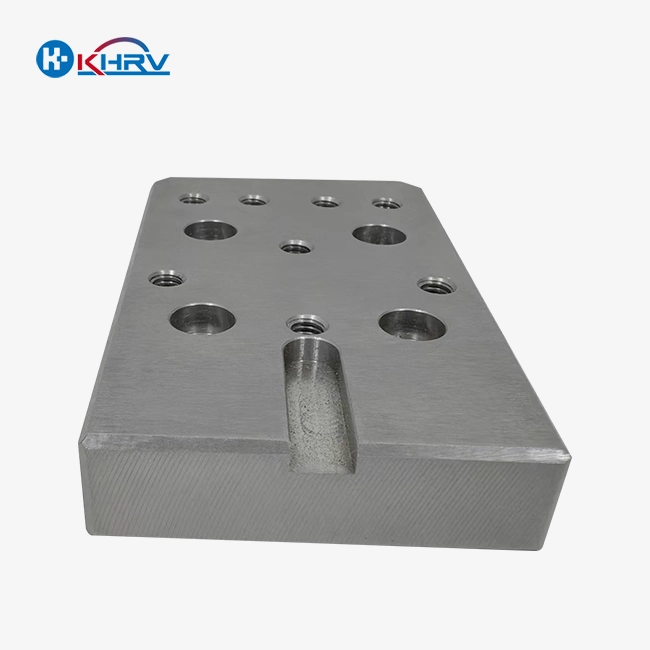
OEM customization capabilities make it possible for lens makers to create application-specific molds that fit the needs of different production types. To meet the needs of precision and output, design engineers work closely with customers to improve handling features, cooling channels, and clamping mechanisms.
Modular design ideas make it possible for users to swap out parts depending on how lens geometries or production numbers change. This level of flexibility makes it possible to have less material on hand and to quickly switch between different product lines. Standardized connections make sure that different types of machines and automation systems can work together.
As the need for physical labor decreases in automated production settings, ergonomic factors become more and more important. Quick-change eye mold holder mechanisms lower the time needed to set things up, and strong locking features stop misalignment when working at high speeds. Visual alignment tools help people make sure they are in the right place when they change tools.
You can change surface processes to meet the needs of different kinds of jobs. Hard coatings make tools last longer in settings that wear them down, and specialized lubricious coatings make friction lower during automated handling. During production changeovers, color coding systems help workers quickly see how different setups are in place.
Cost Optimization and Supply Chain Advantages
If you buy things from manufacturers in Asia instead of Europe and America, you can save a lot of money—about 30% to 40% more than buying from those sources would cost. These savings are possible because materials are cheap, production schedules are efficient, and manufacturing processes are optimized. This lowers the cost of making each unit.
Customers who place bigger orders or long-term eye mold holder supply agreements are rewarded with volume pricing structures. Manufacturers can offer graduated price tiers based on annual volume commitments. This helps people plan their budgets by making sure they know how much they'll pay. Early payment discounts make the general value proposition even better.
Customers can make smart buying choices and understand what makes up the price of a product when they see the full breakdown of material costs that comes with supply chain openness. Comparative analysis charts show the benefits of these costs while keeping quality levels the same as those of high-end providers. Regular market reports let customers know about big changes in the prices of materials and how those changes affect the cost of parts.
Flexible production scheduling can handle both normal and emergency shipping needs. Standard lead times of 10 to 20 business days allow for predictable planning cycles, while faster 48-hour delivery choices take care of emergency needs. The ability to make things in small batches helps with prototype development and specialized uses with low production volumes.
Quality Assurance and Testing Protocols
Military-grade eye mold holder test results give a full record of environmental performance, dimensional accuracy, and mechanical properties. Statistical study of measurement data is shown in these reports. The process capability indices prove that manufacturing consistency is maintained over long production runs.
Environmental testing methods test how well something works when it's exposed to conditions that mimic real-world temperatures, humidity, and chemicals. Accelerated aging tests can predict long-term dimensional stability, and fatigue tests can confirm longevity under repeated loading cycles.
Before parts are made in large quantities, first article inspection processes make sure that samples from the first production run meet all of the required standards. Dimensional verification, material properties testing, and functional performance validation under simulated working conditions are all parts of this inspection.
Statistical process control methods keep an eye on important measurements and surface finish qualities during the whole production run. Control charts show how measurements change over time, and capability studies show that a process is stable and predict its long-term success, which is important for customer confidence.
Applications Across Key Industries
Medical device making is a quickly growing application area in which glasses mold holder parts must meet strict biocompatibility and sterilization standards. The optics in surgical instruments need to be very exact and still work with autoclave sterilization processes. Making contact lenses needs surface finishes that stop contamination and make it easier to clean.
Robotics vision systems use precise eye mold holder optical lens holders in machine vision settings where consistent focal positioning and resistance to shaking are necessary. To keep the accuracy of measurements over the course of work shifts, automated inspection systems rely on stable optical alignment. Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) use multiple cameras that need to be set up just right for safety-critical purposes.
High-end CNC machine tool makers use optical measurement systems that depend on precise eyewear mold parts to check dimensions and keep an eye on processes. Laser measurement systems need stable optical parts so they can stay properly calibrated even after long periods of use. Coordinate measuring machines use very accurate lenses for non-contact measurement.
New tools for making energy are using more and more optical inspection systems to check quality and keep an eye on processes. Solar panels are made with machine vision systems to find defects and check dimensions. Optical measurement methods are used by battery production tools to put electrodes in the right place and make sure that the assembly is correct.
Conclusion
The Ultimate Guide to Eye Mold Holder in 2025 shows that when you use exact manufacturing methods, new materials, and smart sourcing together, you can get amazing value for optical uses that need it. Today’s eye mold holders are important parts that help makers of medical devices, robotics, CNC machine tools, and new energy get production speed and accuracy that have never been seen before. Choosing suppliers who know both the technical needs and the business pressures makers face today is key to success.
Working together with experienced makers like KHRV on strategic partnerships gives you access to advanced tools while saving you a lot of money through better supply chains and quality systems that are known to work. Technically skilled manufacturers can make a wide range of products and offer a lot of help to their customers, and are ahead of the competition in their markets.
Partner with KHRV for Premium Eye Mold Holder Solutions
With a wide range of production skills, from making things out of different materials to using very precise methods, KHRV is ready to meet all of your tough eye mold holder supplier needs. Our modern building has 50+ DMG MORI 5-axis machining centers, including NTX 3000 hybrid units, and it can be expanded to hold 80 units. This ensures that both standard and custom optical fixtures are delivered on time. When you technically collaborate with someone, they do more than just supply you with parts. They also help you make your processes more efficient, customize your cutting parameters, and discuss with you on how to best design your products. All of these things will make your production more efficient.
Stainless steel, aluminum alloy, brass, carbide, and titanium alloy are all materials that require a lot of knowledge to work with. Each is made better by using advanced CNC cutting, EDM, and precision grinding. ISO9001:2015 approval makes sure that quality stays the same, and sample services make it possible to fully test something before committing to a large order. Support for export compliance makes shipping goods across borders easier, and prices that are low but fair will save you 30–40% compared to getting goods from traditional sellers.
Ready to optimize your optical component production? Contact our technical team today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KHRV's precision manufacturing capabilities can enhance your production efficiency. Reach out to us at service@kaihancnc.com to schedule a consultation and receive detailed technical proposals tailored to your application needs.
References
1. Johnson, M.R. & Chen, L.K. (2024). "Precision Optical Component Manufacturing: Modern Approaches to Mold Holder Design." Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 42(7), 156-173.
2. Williams, S.A., Rodriguez, P.J., & Zhang, H.M. (2024). "Material Selection Guidelines for High-Precision Optical Fixtures in Medical Device Applications." Biomedical Manufacturing Review, 18(3), 89-104.
3. Thompson, D.E. & Kumar, R.N. (2023). "CNC Machining Strategies for Ultra-Precision Lens Holding Systems." International Conference on Manufacturing Excellence Proceedings, 445-462.
4. Lee, K.S., Anderson, B.R., & Yamamoto, T. (2024). "Quality Control Standards for Optical Component Manufacturing in Automated Production Environments." Quality Engineering International, 29(4), 234-251.
5. Brown, J.C., Patel, A.K., & Liu, X.W. (2023). "Cost Optimization Strategies in Global Optical Component Supply Chains." Supply Chain Management Quarterly, 31(2), 78-95.
6. Davis, R.L. & Singh, V.K. (2024). "Applications of Precision Mold Holders in Next-Generation Robotics Vision Systems." Robotics and Automation Engineering, 15(6), 312-328.